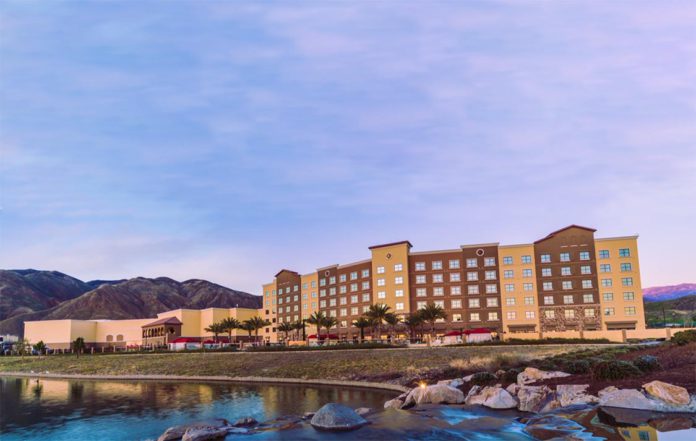
SAN JACINTO, CA – The Soboba Band of Luiseño Indians has prevailed in its effort to overcome the State of California’s failure to negotiate in good faith for a new gaming compact.
Nearly 10 years after it first requested the State of California to negotiate a new Class III gaming compact to replace its original compact with the state, and after the U.S. District Court entered an order finding that the state had failed to negotiate in good faith, the Secretary of the Interior has issued Procedures in lieu of a compact under which the Soboba Band of Luiseño Indians may operate Class III gaming on its tribal lands. The Indian Gaming Regulatory Act (IGRA) authorized the issuance of the Soboba Band’s Secretarial Procedures.
The Secretarial Procedures are a set of regulations that allow a Native American tribe that has obtained a court order determining that a state has failed to negotiate in good faith about a Class III gaming compact to operate Class III gaming, such as slot machines, blackjack, and other casino-style games that are permitted under state law without obtaining a Tribal-State Gaming Compact.
“We’ve always done everything we can to protect our sovereignty; that is something I’ve learned from the leaders that I’ve served under,” said Soboba Tribal Chairman Isaiah Vivanco. “IGRA allows only certain subjects to be included in a compact, and for many years we’ve felt the state was overreaching in our compact negotiations. After about seven years of negotiating and not being able to come to an agreement, we had to sue the state and governor for failure to negotiate in good faith. This became a three-year journey through the court system, followed by negotiations with the Department of Interior, which ultimately led to our Secretarial Procedures being issued on May 10, 2024.”
These procedures serve as a framework to ensure that the Soboba Band’s gaming operations will continue to be conducted in a fair, honest, and transparent manner, benefiting the tribe and the surrounding community economically and otherwise, while maintaining full compliance with strict tribal and federal regulations. Under the Soboba Band’s Secretarial Procedures, the State of California will have no regulatory authority. Compliance with the Procedures will be overseen by the National Indian Gaming Commission (NIGC) instead of the state government.
In California, there are currently 66 casinos operated by 63 tribes. Of the 63 tribes, 50 have Tribal-State Compacts. Thirteen tribes currently operate under Secretarial Procedures rather than under Tribal-State Compacts, having obtained court orders determining that the State of California failed to negotiate in good faith for new compacts.
“Our challenges and wins in the court system may also benefit gaming tribes in the state who have compacts that the Department of the Interior deemed approved to the extent consistent with IGRA,” said Vivanco. “Our win opens up the door for those tribes to approach the state and address provisions in their compacts that are inconsistent with IGRA.”
Under IGRA, the purpose of Secretarial Procedures is to enable a tribe that hasn’t been able to obtain a Class III gaming compact due to a state’s failure to negotiate in good faith to conduct well-regulated Class III gaming in accordance with federal standards. This process involves detailed rules and oversight mechanisms designed to protect the integrity of gaming operations and to ensure that gaming revenues are used for the benefit of the tribes and their communities.
“We have the right to determine for ourselves what’s best for our business,” said Vivanco. “Many compacts have strict restrictions when it comes to growth or expansion; under our Procedures we have the ability to make those decisions when it best suits us. That’s sovereignty – the right to govern ourselves and the ability to grow at our own pace.”
What it means for patrons of the Soboba Casino is more exciting gaming enhancements in the future,” said Jason Cozart, Soboba Casino Resort GM. “Under the Secretarial Procedures, Soboba is no longer limited to a specific number of gaming devices or gaming locations. Importantly, the tribe has the sole authority to determine the number of gaming devices and facilities we can support based on the market we serve.”
IGRA requires that tribes create independent tribal gaming regulatory agencies, and that revenue generated from gaming activities must be used primarily for tribal government operations, economic development, and general welfare of the tribe and its members. The tribe must maintain accurate financial records of all gaming activities. Annual audits by an independent certified public accountant are required to ensure transparency and accountability. Under Secretarial Procedures, the NIGC has oversight authority over the tribes’ regulatory and operational activities.
Gaming operations significantly contribute to the tribe’s economic development, providing funds for infrastructure, healthcare, education, and social services. The Soboba Casino Resort (SCR) will continue to create job opportunities for tribal members and the local community, fostering economic self-sufficiency and growth. Funds generated from gaming will support local government services such as law enforcement, fire protection, and public works, benefiting the wider community.
These pocedures ensure that the Soboba Band of Luiseño Indians can operate its gaming facilities in a way that is beneficial to the reservation community, while maintaining high standards of integrity and compliance with all applicable laws. This approval marks a significant step forward for the tribe, providing the tribal government and citizens with new opportunities for economic development and community support.
“There are certainly expenses that are no longer required to be paid to the state,” said Cozart. “The tribe, with the guidance of Tribal Council and Executive Management here at SCR will determine the best way to reallocate available resources to key components of our business.”
Overall, the Secretarial Procedures provide a streamlined and federally regulated pathway for tribes to engage in gaming activities, promoting economic development and self-sufficiency for Native American communities.